Examples of Outcomes
Poor Examples:
At the conclusion of the course students will be able to…
- ...appreciate the benefits of exercise
- ...access resources at IVC
- ...have more confidence in their abilities
Better Examples:
At the conclusion of the course students will be able to…
- ...explain how exercise affects stress
- ...identify the most appropriate resource that is pertinent to their IVC concern
- ...demonstrate the ability to analyze and respond to arguments about racial discrimination
Creating SLOs Checklist
After creating an SLO reference this checklist:
- Does the outcome support the course objectives?
- Does the outcome describe what the program intends for students to know (cognitive), think (affective, attitudinal), or do (behavioral, performance)?
- Is the outcome important/worthwhile?
- Is the outcome:
- detailed and specific?
- measurable/identifiable?
- a result of learning?
- Do you have or can you create an activity (or multiple activities) to enable students to learn the desired outcome?
- Can the outcome be used to make decisions on how to improve the course?
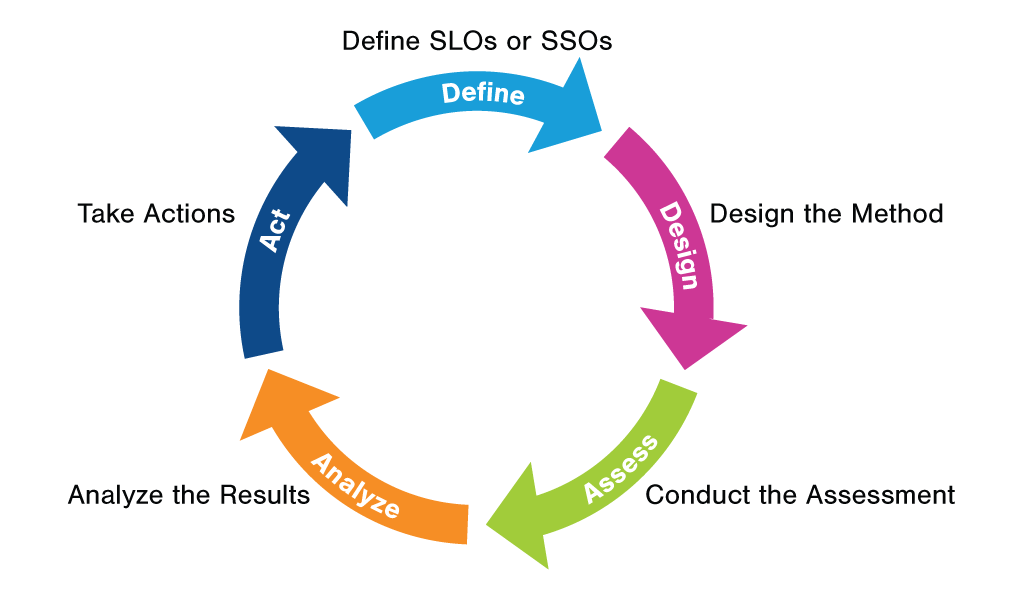
If all of the questions on the checklist are met with a yes, then move onto developing a method assessing the SLO.